-
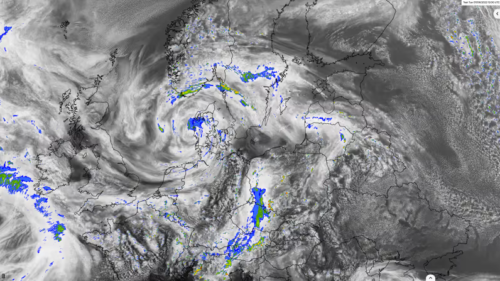 A numerical weather model calculates the current state of the atmosphere and the state of the future with the help of computers and on the basis of measured data, both locally measured and remotely sensed. Complex physical equations are used, which are calculated by high-performance computers with enormous power and processed into high-resolution weather forecasts.
A numerical weather model calculates the current state of the atmosphere and the state of the future with the help of computers and on the basis of measured data, both locally measured and remotely sensed. Complex physical equations are used, which are calculated by high-performance computers with enormous power and processed into high-resolution weather forecasts. -
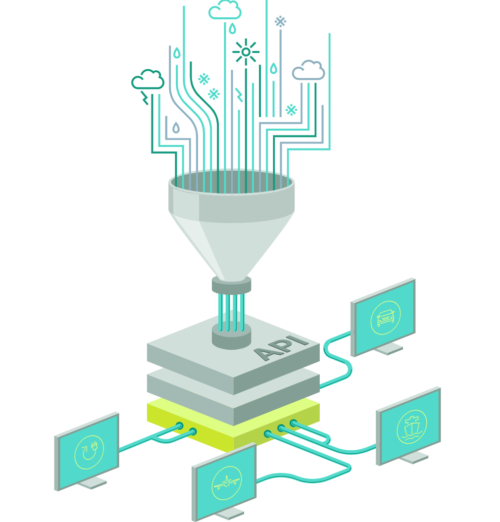 An API (Application Programming Interface) provides an interface for various programming languages that allows developers and programmers to integrate the data directly into their systems in the desired format in just a few steps. The Meteomatics weather API contains data on weather and climate. It provides access to over 25 weather models (e.g. GFS, ECMWF, DWD, MeteoFrance, UKMetoffice and many more) and more than 1800 weather parameters. Our interface is thus considered the gateway to the largest database of historical weather data, forecast data and climate data worldwide.
An API (Application Programming Interface) provides an interface for various programming languages that allows developers and programmers to integrate the data directly into their systems in the desired format in just a few steps. The Meteomatics weather API contains data on weather and climate. It provides access to over 25 weather models (e.g. GFS, ECMWF, DWD, MeteoFrance, UKMetoffice and many more) and more than 1800 weather parameters. Our interface is thus considered the gateway to the largest database of historical weather data, forecast data and climate data worldwide. -
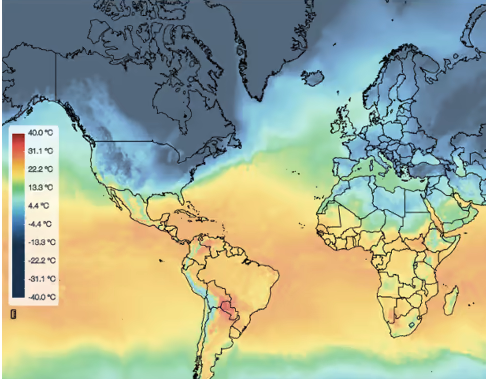 The weather events depicted can be past, present or forecast for the future. From a meteorological point of view, a weather map shows the current state of the atmosphere over a larger area. A weather map can provide information about certain weather parameters, such as temperature, wind speed, wind direction or precipitation. The weather observations or expected changes in the state are drawn in symbolic form or coloured contours.
The weather events depicted can be past, present or forecast for the future. From a meteorological point of view, a weather map shows the current state of the atmosphere over a larger area. A weather map can provide information about certain weather parameters, such as temperature, wind speed, wind direction or precipitation. The weather observations or expected changes in the state are drawn in symbolic form or coloured contours.

