-
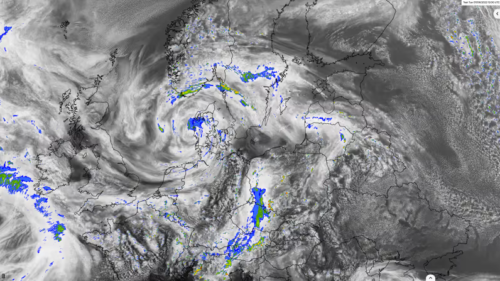 A numerical weather model calculates the current state of the atmosphere and the state of the future with the help of computers and on the basis of measured data, both locally measured and remotely sensed. Complex physical equations are used, which are calculated by high-performance computers with enormous power and processed into high-resolution weather forecasts.
A numerical weather model calculates the current state of the atmosphere and the state of the future with the help of computers and on the basis of measured data, both locally measured and remotely sensed. Complex physical equations are used, which are calculated by high-performance computers with enormous power and processed into high-resolution weather forecasts. -
 An API (Application Programming Interface) provides an interface for various programming languages that allows developers and programmers to integrate the data directly into their systems in the desired format in just a few steps. The Meteomatics weather API contains data on weather and climate. It provides access to over 25 weather models (e.g. GFS, ECMWF, DWD, MeteoFrance, UKMetoffice and many more) and more than 1800 weather parameters. Our interface is thus considered the gateway to the largest database of historical weather data, forecast data and climate data worldwide.
An API (Application Programming Interface) provides an interface for various programming languages that allows developers and programmers to integrate the data directly into their systems in the desired format in just a few steps. The Meteomatics weather API contains data on weather and climate. It provides access to over 25 weather models (e.g. GFS, ECMWF, DWD, MeteoFrance, UKMetoffice and many more) and more than 1800 weather parameters. Our interface is thus considered the gateway to the largest database of historical weather data, forecast data and climate data worldwide. -
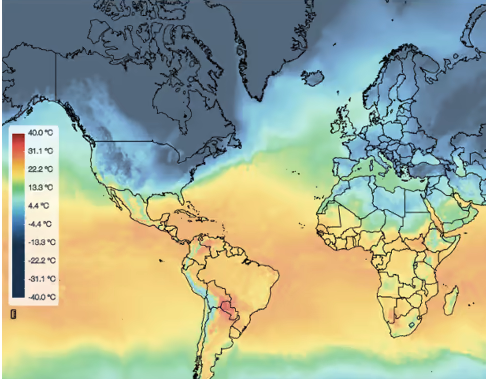 The weather events depicted can be past, present or forecast for the future. From a meteorological point of view, a weather map shows the current state of the atmosphere over a larger area. A weather map can provide information about certain weather parameters, such as temperature, wind speed, wind direction or precipitation. The weather observations or expected changes in the state are drawn in symbolic form or coloured contours.
The weather events depicted can be past, present or forecast for the future. From a meteorological point of view, a weather map shows the current state of the atmosphere over a larger area. A weather map can provide information about certain weather parameters, such as temperature, wind speed, wind direction or precipitation. The weather observations or expected changes in the state are drawn in symbolic form or coloured contours. -
 We offer detailed forecast systems and individual solutions, which we refine locally on the basis of high-resolution weather model data. Local conditions as well as live data from the respective power plants are included in our energy forecasts. This enables us to make precise energy forecasts for wind, solar and hydropower feed-in for different control areas and locations.
We offer detailed forecast systems and individual solutions, which we refine locally on the basis of high-resolution weather model data. Local conditions as well as live data from the respective power plants are included in our energy forecasts. This enables us to make precise energy forecasts for wind, solar and hydropower feed-in for different control areas and locations. -
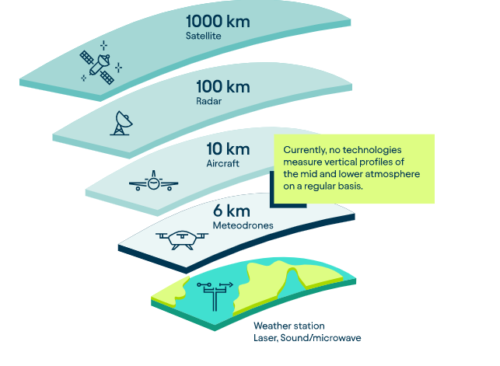 The specially developed, patented Meteodrones operated by our drone pilots offer the innovative possibility to collect weather data from the lower and middle atmosphere. With Meteodrones, it is possible for the first time to carry out high-resolution and direct measurements of temperature, humidity, air pressure and wind, to incorporate these into weather model calculations and thus demonstrably improve weather forecasts.
The specially developed, patented Meteodrones operated by our drone pilots offer the innovative possibility to collect weather data from the lower and middle atmosphere. With Meteodrones, it is possible for the first time to carry out high-resolution and direct measurements of temperature, humidity, air pressure and wind, to incorporate these into weather model calculations and thus demonstrably improve weather forecasts. -
 An important step towards nationwide drone deployment was the development of the Meteobase. It enables autonomous drone measurements and is also the drone's "home" from which it takes off, lands and its battery is charged. As a ground station, it serves as local support for the operation of the Meteodrones. It serves as a communication element between the pilot and the drone or works as a control element for autonomous flights of the drone. The Meteobase consists of a central computer that performs various tasks related to the operation, control and maintenance of the drone and the monitoring and logging of weather parameters at the site.
An important step towards nationwide drone deployment was the development of the Meteobase. It enables autonomous drone measurements and is also the drone's "home" from which it takes off, lands and its battery is charged. As a ground station, it serves as local support for the operation of the Meteodrones. It serves as a communication element between the pilot and the drone or works as a control element for autonomous flights of the drone. The Meteobase consists of a central computer that performs various tasks related to the operation, control and maintenance of the drone and the monitoring and logging of weather parameters at the site.

